How Accurate is Google Translate? An In-Depth Look for Businesses
In a world where cross-border communication is vital for growth, Google Translate is often one of the first tools that comes to mind. It’s fast, free, and available to anyone with an internet connection. But as businesses become more globally connected, relying solely on convenience can have serious consequences. So how accurate is Google Translate, really? And more importantly, is it the right tool for translating your business website or marketing content?
Let’s unpack how Google Translate works, its current strengths and weaknesses, and how platforms like MultiLipi take the power of machine translation and amplify it with human-like precision for global-ready content.
How Google Translate Works: The Technology Behind It
Google Translate was introduced in 2006 using statistical machine translation (SMT). It primarily translated by analyzing patterns in large amounts of bilingual text. While this worked for simple phrases, it often produced garbled or misleading outputs for more complex content.
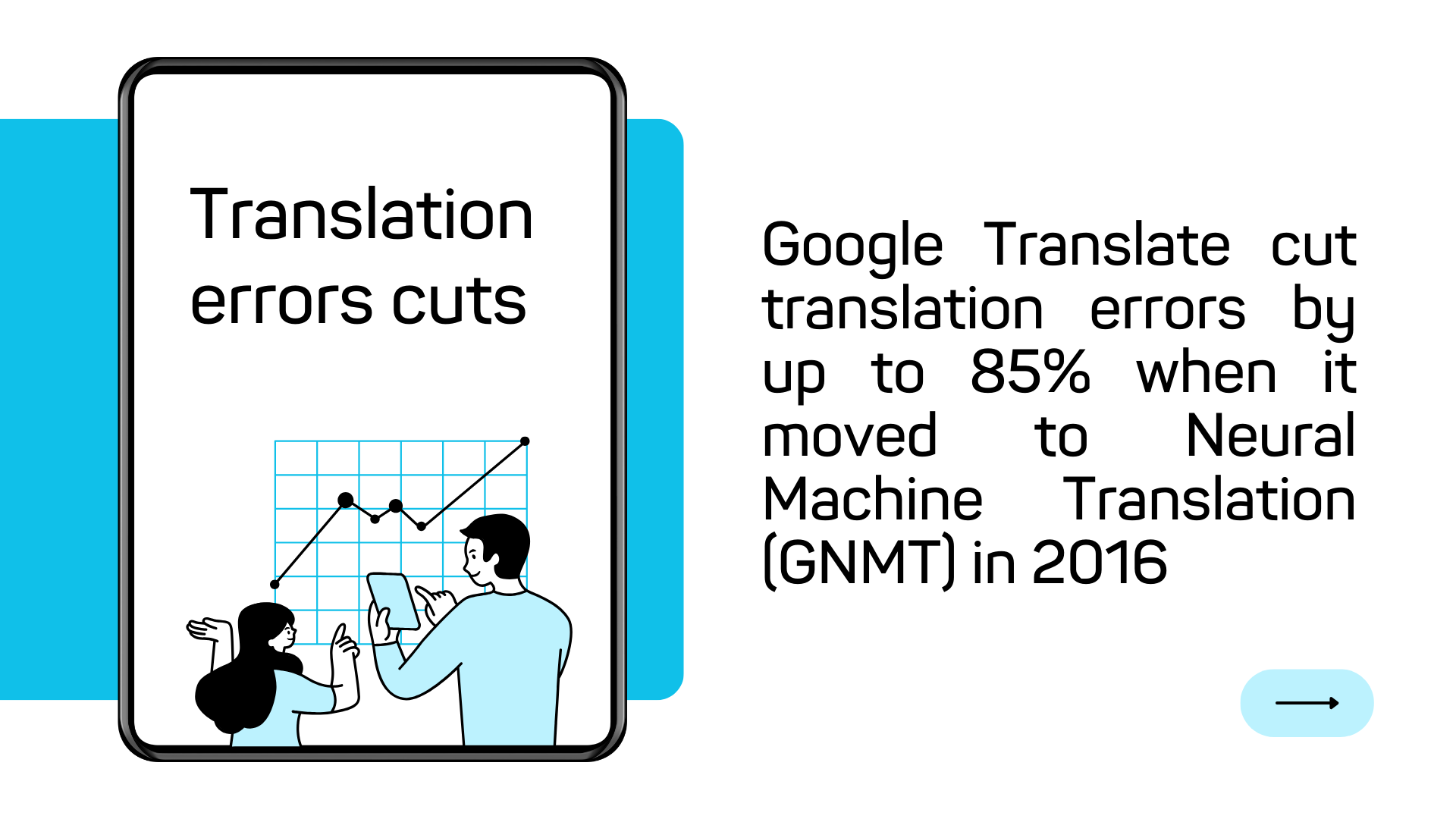
Fast forward to 2016, and Google replaced SMT with Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT). Instead of translating word by word, GNMT uses deep learning to evaluate entire sentences. This context-based approach made translations much more fluent and accurate. Google also stopped using English as an intermediary language, opting instead for direct translations between source and target languages.
This shift dramatically improved accuracy—Google reported a 55-85% reduction in translation errors for major language pairs. For instance, French to Japanese translations became faster and more reliable without passing through English.
However, while GNMT marked a turning point, its performance still depends heavily on language data availability. Common languages with extensive online data, like Spanish and English, yield much better results than lesser-used ones like Swahili or Urdu.
Is Google Translate Accurate? It Depends.
As of 2025, Google Translate supports over 130 languages, making it one of the most widely accessible machine translation tools. Yet accuracy varies significantly.
A 2021 study by UCLA Medical Center found that Google Translate preserved the overall meaning in 82.5% of cases across 26 languages. The accuracy, however, ranged from just 55% to 94%, depending on the language pair. Spanish, being widely used, typically enjoys over 90% accuracy, while languages like Armenian or Khmer fall on the lower end of the spectrum.
Interestingly, Google Translate performs best when converting literary or structured content into English. But it struggles with slang, idioms, and informal phrases—like turning English expressions into Japanese or Hindi, where context plays a huge role.
MultiLipi’s internal studies mirror these findings. In user testing, 10 out of 14 professional translators were pleasantly surprised by machine-translated drafts. But even then, every output required some degree of post-editing to ensure nuance, cultural tone, and business relevance were preserved.
Can Google Translate Handle Website Translations?
Here’s the thing: speed is not always your best friend. Businesses might be tempted to use Google Translate to convert their entire site in seconds. But the risks of content being misunderstood or misrepresented are very real.
For example, if context isn’t correctly identified, Google Translate might use a generic meaning for a term that has specific industry or cultural significance. This is especially problematic for eCommerce platforms, legal disclaimers, medical services, and financial sites.
What’s more, Google discontinued its community “Contribute” feature, which used to rely on native speakers to improve translation quality. Without this, the platform now relies solely on AI models trained on existing data—which may or may not reflect the most accurate or culturally sensitive language usage.
Statistically, English translations remain its strongest suit, thanks to English dominating over 50% of indexed websites. But for Portuguese, Hindi, or Arabic—languages with lower web presence—accuracy drops considerably.
Why Does This Matter for Your Business?
Because 73% of consumers prefer product reviews and websites in their native language. If your messaging feels "off" or sounds robotic, you risk losing trust. That’s why localization—the process of translating and culturally adapting content—is essential.
MultiLipi addresses this by integrating neural machine translation with human validation. Our platform goes beyond translating words. It understands tone, region-specific usage, and brand guidelines—creating experiences that speak to your audience, not just at them.
Comparing Google Translate to Other MT Tools
In a benchmark study conducted by Nimdzi and Weglot, translation accuracy among popular platforms was evaluated:
- DeepL had the fewest "unacceptable" outputs but also the fewest "no-touch" translations (ready-to-publish) for Italian. It excels in European language pairs but only supports 28 languages.
- Amazon Translate surprisingly performed best in French, producing the highest number of no-touch outputs, while also offering accurate Chinese translations. It supports 75 languages.
- Microsoft Translator covers 111 languages and offers solid consistency, particularly with German and Arabic, though it fell short with Portuguese.
What’s the takeaway? No tool is perfect. Each has strengths depending on the language and content type. That's why MultiLipi lets you choose the best MT engine per language pair—then enriches it with human feedback.
When Should You Use Google Translate?
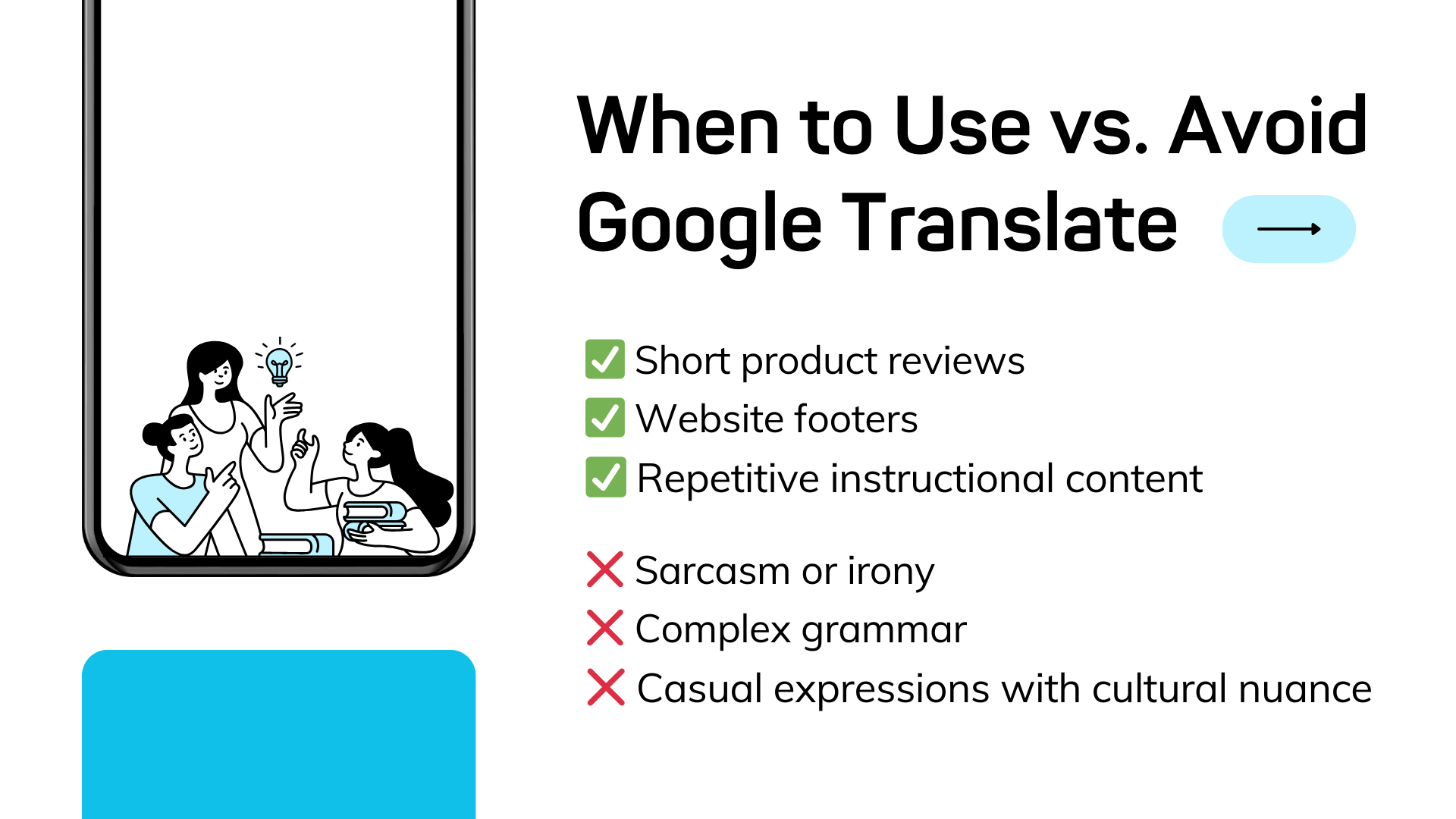
Google Translate works well for:
- Low-risk, low-visibility text like footers or error messages.
- Repetitive instructional content (e.g., navigation guides).
- Product reviews where basic understanding is enough.
But avoid using it for:
- Idiomatic expressions or sarcastic phrases.
- Industry-specific jargon or regulatory text.
- Highly creative or brand-driven marketing copy.
The Power of Machine Translation + Human Editing

According to recent research, 99% of global translation output is machine-generated—and only 30% is professionally edited. That leaves a massive opportunity for businesses that want to gain an edge.
At MultiLipi, we bridge this gap. Our AI-human hybrid model ensures content is not just translated, but localized with cultural empathy and SEO optimization.
We automate tedious processes, leverage the best of GNMT, DeepL, and more, and back every translation with native-language reviewers who know your market.
If you're serious about multilingual SEO and brand consistency, relying solely on Google Translate isn’t enough. With MultiLipi, you don’t just translate—you communicate, connect, and convert.
Curious about how your current translations hold up? Try MultiLipi’s demo and get your first page translated and localized.

